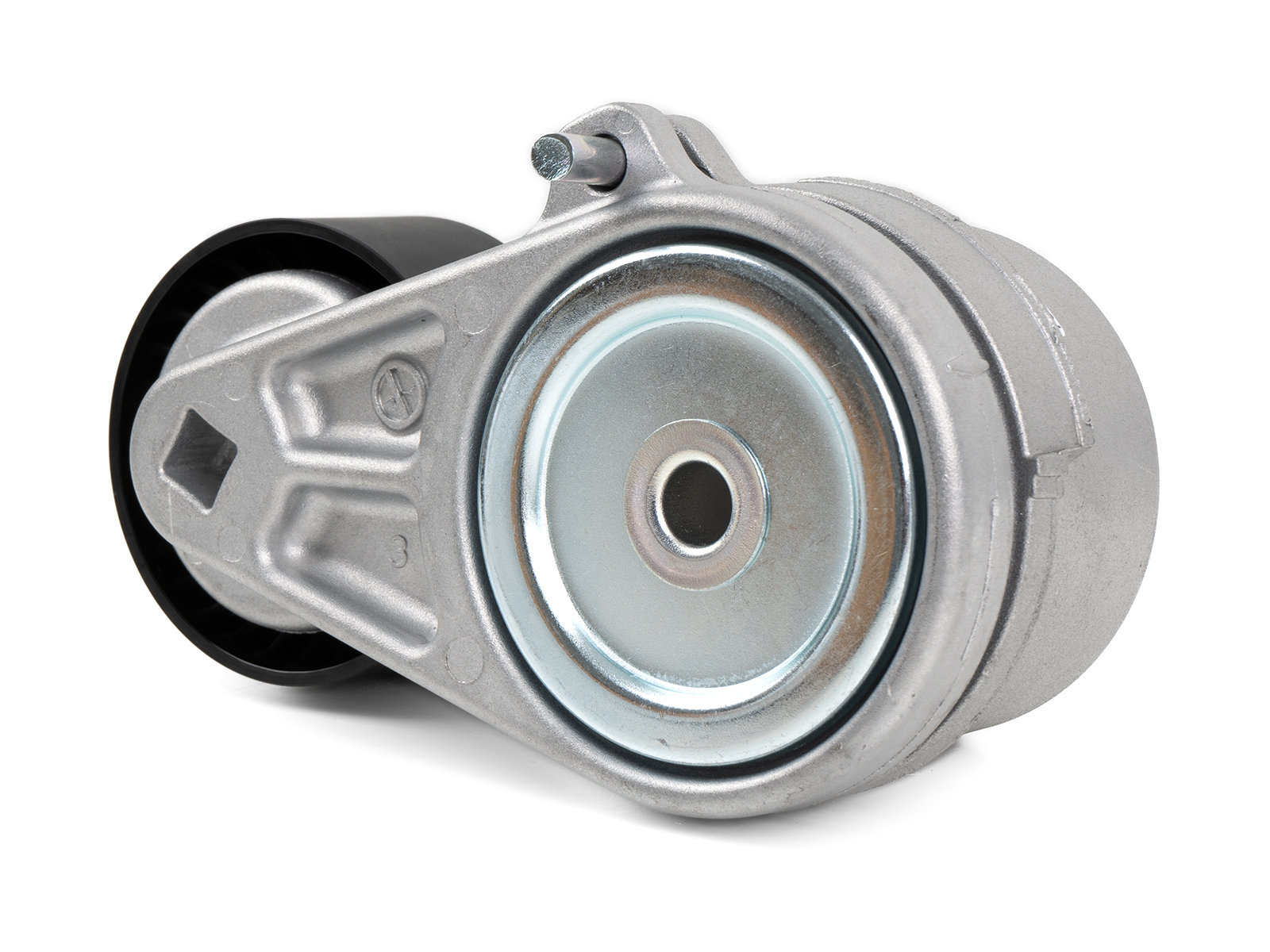
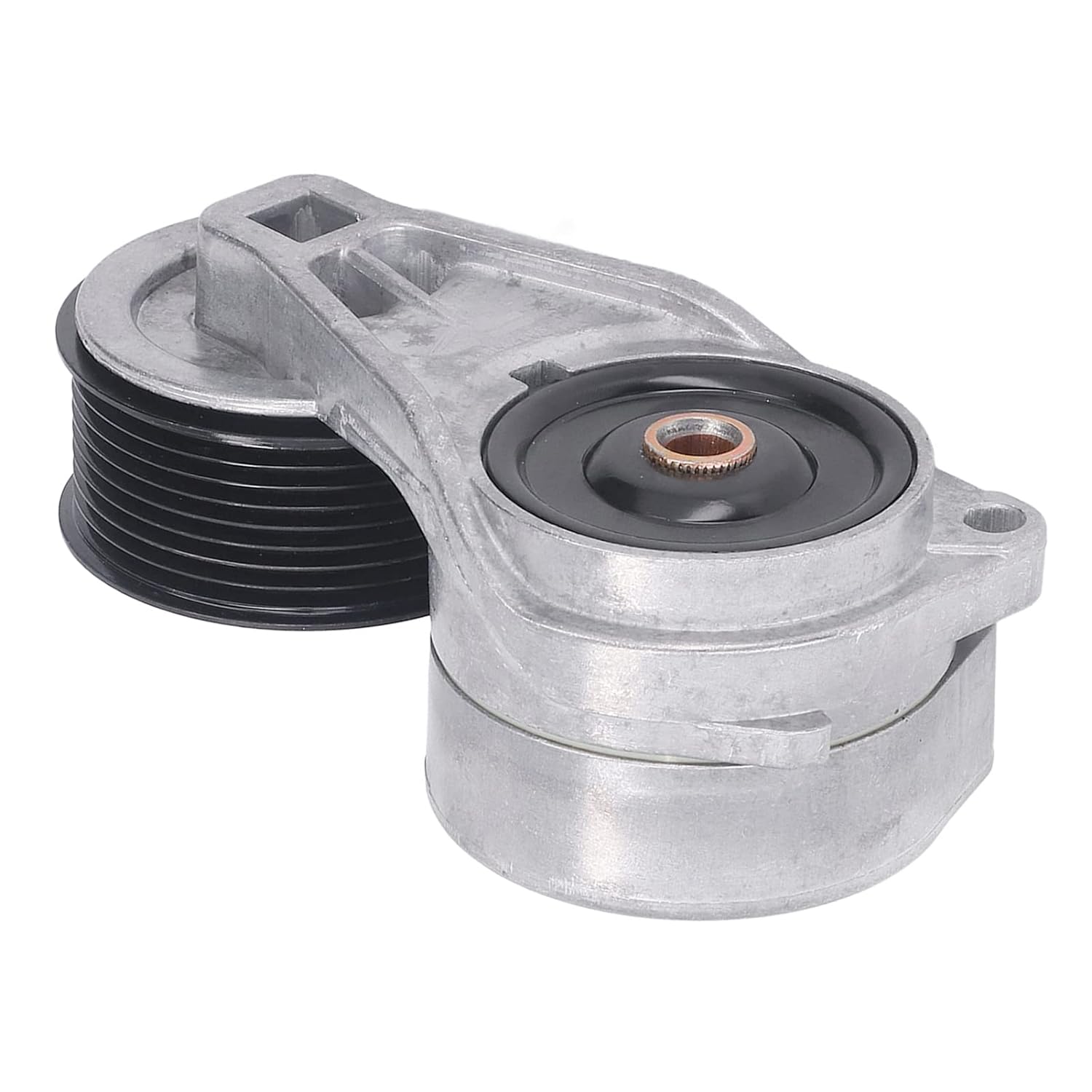
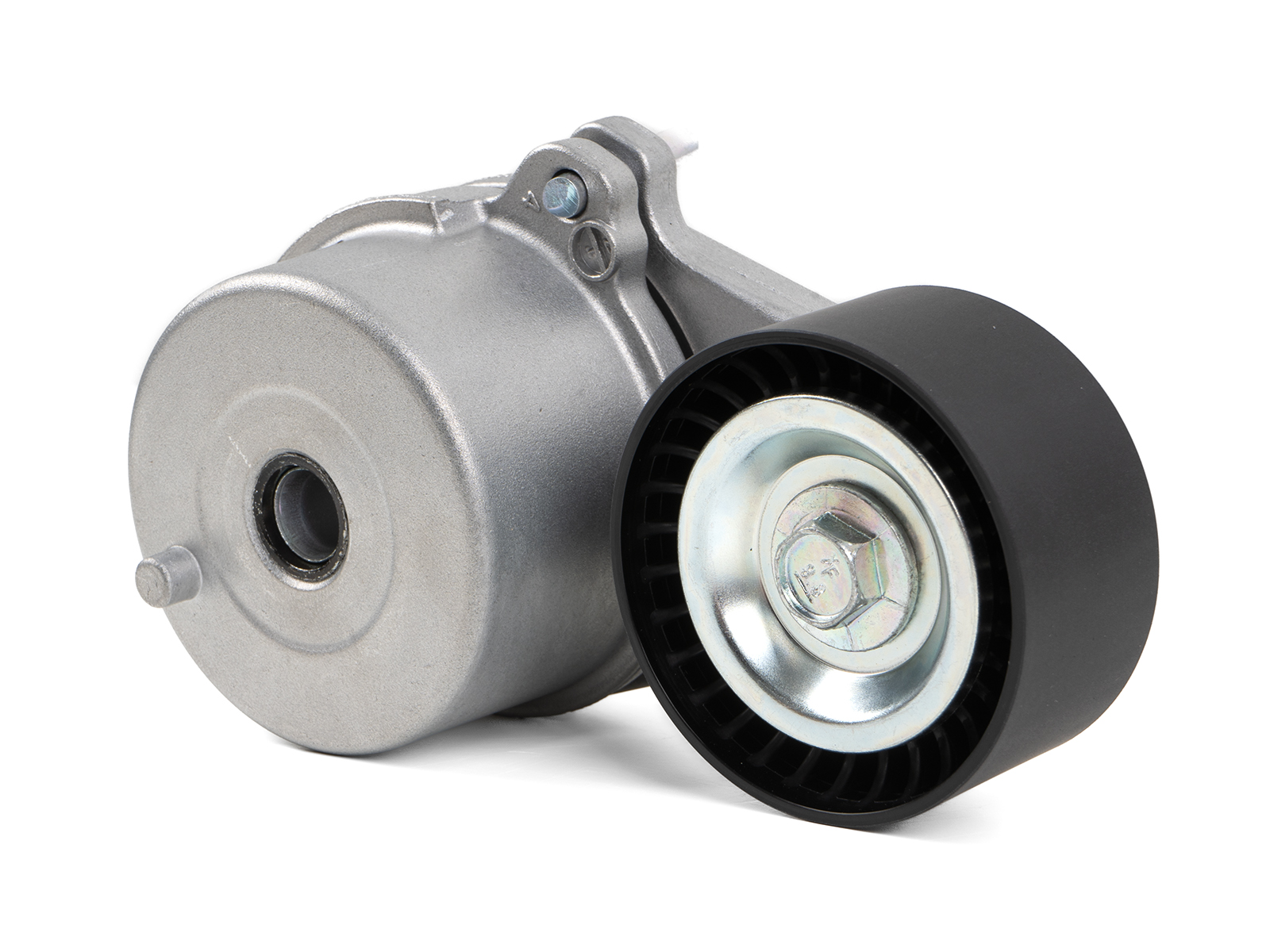
Product Description
Hotselling
Packaging & Shipping
Our Advantages
Company Profile
Exhibition
Payments
Main products
FAQ
Q1. Which package do you used ?
A: Generally we pack our goods in neutral or white boxes and brown cartons. Your own brand and and logo are welcomed after getting your authorization letter.
Q2. What ‘s your payment way?
A: T/T 30% advance, and 70% after send photos of goods to you before load .
Q3. What ‘s the delivery way ?
A: We accept EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DDU,just as your wish .
Q4. How long is your delivery time?
A: Usually it will take about 30 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q5. What can i do if i received bad products ?
A: We will think highly of your feedback ,Please contact our sales at once if you find any problems after you received goods, our sales will give you resonable reply and help you solve all problems .
Q6. What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers has to pay the sample cost and the delivery cost.
Q7. Do you test all your goods before the delivery?
A: Yes, we do test and complete our tests 100% before the delivery.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Quality Gurranted |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 6 Months |
| Type: | Tensioner Bearing |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Tolerance: | P0 |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |

Can you provide guidance on the selection and sizing of belt tensioners for specific belt applications?
When selecting and sizing belt tensioners for specific belt applications, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed guidance on the selection and sizing of belt tensioners:
- Belt Type and Size:
- System Requirements:
- Tensioner Type:
- Tensioner Design and Mounting:
- Tensioner Load Capacity:
- Environmental Considerations:
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
Start by identifying the type and size of the belt used in the application. Belts can vary in terms of width, length, profile (V-belt, timing belt, etc.), and construction material (rubber, polyurethane, etc.). The tensioner should be compatible with the specific belt type and size to ensure proper fit and functionality.
Consider the requirements of the belt-driven system. Evaluate factors such as the desired tension level, operating speed, load conditions, and environmental factors. The tensioner should be capable of providing the required tension force while accommodating the system’s operating parameters.
Choose the appropriate tensioner type based on the application’s needs. Common types include automatic tensioners, idler pulley tensioners, spring-loaded tensioners, and hydraulic tensioners. Each type has its advantages and limitations, so select the one that best suits the specific belt application.
Consider the design and mounting requirements of the tensioner. Evaluate the space availability, mounting configuration, and alignment with other components in the belt drive system. Some tensioners offer adjustable mounting positions or different design variations to accommodate various installation scenarios.
Check the load capacity of the tensioner to ensure it can handle the expected loads and forces in the belt system. Consider factors such as the belt tension, shock loads, and dynamic forces. The tensioner should have adequate load capacity to prevent premature wear or failure under normal operating conditions.
Assess the environmental conditions in which the tensioner will operate. Factors such as temperature extremes, moisture, dust, chemicals, and exposure to UV radiation can impact the tensioner’s performance and durability. Choose a tensioner that is designed to withstand the specific environmental challenges of the application.
Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for selecting and sizing the tensioner. Manufacturers often provide technical data, specifications, and selection guides that assist in choosing the appropriate tensioner for specific belt applications. Follow their recommendations to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
It is important to note that the selection and sizing of belt tensioners may require technical expertise and consideration of specific application requirements. If in doubt, consult with belt tensioner manufacturers or industry experts who can provide further guidance based on their knowledge and experience.
In summary, when selecting and sizing belt tensioners for specific belt applications, consider the belt type and size, system requirements, tensioner type, design and mounting, load capacity, environmental conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a suitable tensioner that ensures proper tensioning, reliable operation, and extended belt life in the belt-driven system.

Can you explain the principles behind belt tensioner operation and adjustment?
Belt tensioners operate based on a set of principles aimed at maintaining the proper tension in belts. They are designed to apply and control the tension in the belt drive system, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the principles behind belt tensioner operation and adjustment:
- Tensioning Mechanism:
- Proper Tension Range:
- Belt Deflection:
- Adjustment and Maintenance:
- Monitoring and Inspection:
- Consideration of Environmental Factors:
Belt tensioners typically consist of a mechanical mechanism that applies force to the belt, adjusting its tension. The tensioning mechanism can vary depending on the specific design and application. Common types of tensioners include spring-loaded tensioners, hydraulic tensioners, and automatic tensioners. These mechanisms are designed to exert a specific amount of force on the belt, maintaining the desired tension level.
Each belt has a specific tension range recommended by the manufacturer. This range ensures optimal power transmission, minimal slippage, and reduced wear. Belt tensioners are adjusted to operate within this recommended tension range. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or specifications to determine the appropriate tension for a specific belt and application.
During operation, belts experience a certain degree of deflection or sag between the pulleys. Belt tensioners account for this deflection and compensate for it by applying the appropriate tension. The tensioner mechanism is adjusted to ensure that the belt maintains the desired tension even when subjected to deflection. This helps to prevent excessive slack or tightness in the belt, optimizing power transmission and minimizing wear.
Belt tensioners require periodic adjustment and maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The adjustment process involves inspecting the belt tension, evaluating its deflection, and making necessary adjustments to bring it within the recommended tension range. Tensioners may feature adjustment bolts, nuts, or other mechanisms that allow for precise tension adjustments. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use appropriate tools to adjust the tensioner correctly.
Regular monitoring and inspection of belt tensioners are crucial for their effective operation. This involves visually examining the tensioner for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. It is also important to check the belt tension regularly using appropriate tension measuring tools or techniques. By monitoring the tensioner and the belt’s condition, any issues can be identified and addressed promptly, ensuring optimal tension and preventing potential problems.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and operating conditions can influence belt tension. Belt tensioners should be adjusted and maintained considering these factors. For example, temperature changes can cause the belt to expand or contract, affecting its tension. Tensioners may incorporate features to compensate for such variations, ensuring consistent tension under different environmental conditions.
In summary, belt tensioner operation and adjustment are based on principles that involve applying the appropriate tension to the belt, accounting for deflection, operating within the recommended tension range, and considering environmental factors. Tensioners are adjusted and maintained to ensure optimal power transmission, minimize wear, and prevent issues such as slippage or excessive tension. Regular monitoring and inspection of tensioners and belts are essential for their reliable operation and longevity.

Can you describe the various types of belt tensioners, such as automatic or manual tensioners?
There are various types of belt tensioners available, each designed to fulfill specific requirements in maintaining belt tension. Here’s a description of the different types of belt tensioners:
- Manual Belt Tensioners:
- Automatic Belt Tensioners:
- Hydraulic Belt Tensioners:
- Eccentric Belt Tensioners:
- Idler Pulley Tensioners:
Manual belt tensioners are the most basic type and require manual adjustment to set and maintain the desired tension. They typically consist of an adjustable arm or bracket that can be moved to increase or decrease the tension in the belt. Manual tensioners are commonly used in applications where tension adjustments are infrequent or can be easily accessed for manual adjustment. They are simple, cost-effective, and widely used in various industries.
Automatic belt tensioners, also known as self-adjusting or spring-loaded tensioners, are designed to maintain the proper tension automatically. They incorporate a spring mechanism that applies constant tension to the belt, compensating for belt elongation and wear over time. Automatic tensioners are commonly used in applications where frequent manual adjustments are impractical or where consistent tension control is essential. They provide convenience, minimize maintenance requirements, and ensure optimal tension without the need for manual intervention.
Hydraulic belt tensioners utilize hydraulic pressure to maintain belt tension. They consist of a hydraulic cylinder or piston that applies force to the tensioner arm, adjusting the tension in the belt. Hydraulic tensioners are commonly used in applications with high load requirements or variable operating conditions. They provide precise tension control, can compensate for changes in temperature and load, and are often employed in heavy-duty industrial machinery and automotive applications.
Eccentric belt tensioners use an eccentric mechanism to adjust the tension in the belt. They typically feature an eccentric pulley or roller that can be rotated to increase or decrease the tension. Eccentric tensioners are commonly used in applications where precise tension adjustments are required, such as high-performance engines or systems with specific belt tension specifications. They offer fine-tuning capabilities and are often found in automotive racing, performance tuning, and specialized machinery.
Idler pulley tensioners, also known as fixed tensioners or idler pulley assemblies, are a type of belt tensioner that utilizes an idler pulley to maintain tension. They are typically positioned on the slack side of the belt, providing guidance and tension control. Idler pulley tensioners are commonly used in applications where a fixed tension is desired, and the tensioning capability is provided by other components in the system, such as an automatic tensioner or an adjustable drive pulley.
In addition to these types, there are also specialized belt tensioners designed for specific applications or industries, such as torsional vibration dampers used in automotive engines to reduce vibrations, or belt tensioners with built-in dampening mechanisms to minimize noise in certain applications.
Overall, the choice of belt tensioner depends on factors such as the application requirements, load conditions, frequency of tension adjustments, and the desired level of automation and control. Selecting the appropriate type of belt tensioner is crucial to maintaining optimal belt tension and ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of belt-driven systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China Best Sales 6204 Bearings High Speed Deep Groove Ball Bearing for Agriculture Machine near me manufacturer
Product Description
QUICK OVERVIEW
| Model | Deep Groove Ball Bearing |
| Greese/Oil | As your requirement, such as open, z,zz,rz, 2rz,rs, 2rs, and so on. |
| Vibration | Z1/V1,Z2/V2,Z3/V3 |
| Tolerance codes | ABEC-1, ABEC-3, ABEC-5, ABEC-7 |
| Internal clearance codes | C0, C2, C3, C4, C5 |
| Snap ring | N, NR |
| Quality level | Reach the same level as Japanese and European bearings, P0 P2 P4 P5 P6.. |
| Feature | Low voice, High speed, Low friction, long service life |
| Application | Pharmaceutical equipment, medical equipment, textile machinery and accessories, knitting machines, weaving machines, spinning equipment, textile accessories, non-woven fabric machinery, textile equipment, machinery, metal, mold, automotive electronics, electrical, instrumentation, military, aviation aerospace, plastics and rubber industry, medical and other fields. |
| Package | 1,barreled package+outer carton+pallets 2,single box+outer carton+pallets 3,tube package+middle box+outer carton+pallets 4,According to your’s requirement |
| Details | We have a complete process for production and quality assurance to make sure our products can meet your requirement. 1.Assembly 2.Windage test 3.Cleaning 4.Rotary test 5.Greasing and gland 6.Noise inspection 7.Appearance inspection 8.Rust prevention |
Deep groove ball bearings are the most representative structure in rolling bearings and have been widely used in many industries, such as cars, compressors, construction, electric motors, food industry, home appliances, etc. They are suitable for high or even extremely high-speed operation, and very durable, and need not be maintained regularly. This kind of bearing has a small friction coefficient, high limit speed. Widely used in industrial machinery, automobile, electrical system.
Application and popular suitable models:
1.Motorcycle rear wheel bearing: 63032RS, 6302 2RS
2.High-speed ball bearing for electric tools: 628ZZ, 688ZZ
3.Bearing for electric motor: 6204 2RS, 6205 2RS
4.Skateboard rubber roller bearings: 608 2RS, 6072RS, 6092RS, 6282RS
5.Stainless steel deep groove ball bearings for the food industry: S6900 2RS, S6901 2RS
6.Ceiling fan bearing: 6202 ZZ, 6203 ZZ
7.Thin wall deep groove ball for sweeper: 6900, 6800 series
Pictures
Model List (Please contact with us for more models)
| Product | Bore Dia (d) (mm) | Outer Dia (D) (mm) | Width (B) (mm) | Radius (min) (rs) (mm) | Dynamic Load Rating (Cr) (N) | Static Load Rating (Cor) (N) |
| 6000 | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 4,550 | 1,950 |
| 6000-2RS | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 4,550 | 1,950 |
| 6000ZZ | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 4,550 | 1,950 |
| 6200 | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6200-2RS | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6200ZZ | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6300-2RS | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6300ZZ | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6001-2RS | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6001ZZ | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6201 | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6,800 | 3,050 |
| 6201-2RS | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6,800 | 3,050 |
| 6201ZZ | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6,800 | 3,050 |
| 6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 9,700 | 4,200 |
| 6301-2RS | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 9,700 | 4,200 |
| 6301ZZ | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 9,700 | 4,200 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 5,600 | 2,850 |
| 6002-2RS | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 5,600 | 2,850 |
| 6002ZZ | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6202 | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 7,650 | 3,750 |
| 6202-2RS | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 7,650 | 3,750 |
| 6202ZZ | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 7,650 | 3,750 |
| 6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 11,400 | 5,450 |
| 6302-2RS | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 11,400 | 5,450 |
| 6302ZZ | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 11,400 | 5,450 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6,000 | 3,250 |
| 6003-2RS | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6,000 | 3,250 |
| 6003ZZ | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6,000 | 3,250 |
A wide range of applications:
• agriculture and forestry equipment
• automotive and industrial gearboxes
• automotive and truck electric components, such as alternators
• electric motors
• fluid machinery
• material handling
• power tools and household appliances
• textile machinery
• two Wheeler.
Our Bearing Advantage:
1.ISO Standard
2.Bearing Small order accepted
3.In Stock bearing
4.OEM bearing service
5.Professional:20 years manufacture bearing
6.Customized bearing, Customer’s bearing drawing or samples accepted
7.Competitive price bearing
8.TT Payment or Western Union or PayPal
Our Company
| Packaging Details | 1 piece in a single box 50 boxes in a carton 20 cartons in a pallet |
| Nearest Port | ZheJiang or HangZhou |
| Lead Time | For stock parts: 1-5 days. If no stock parts: <200 pcs: 15-30 days ≥200 pcs: to be negotiated. |
FAQ
1.How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
– We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
– We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
2.Do you test all your goods before delivery?
– Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
3.What products does your company supply?
– Auto Bearings (Wheel Bearings, Wheel Hub Bearings, Clutch Bearings, Belt Tensioners and Water Pump Bearings etc. )
-Industrial Bearings (Deep Groove Ball Bearings, Tapered Roller Bearings and Pillow Block Bearings).
What to Look for in a Belt Tensioner
If you notice the power steering, air conditioning, or power steering stops working, chances are that your belt tensioner has been compromised. A compromised belt tensioner can be completely destroyed overnight, or it can last for a long time before it breaks. Either way, you should never drive with a faulty belt tensioner. It’s far better to have it replaced before the engine shuts down completely. In addition, replacing a belt tensioner will prevent other complications, such as power steering or air conditioning, from occurring.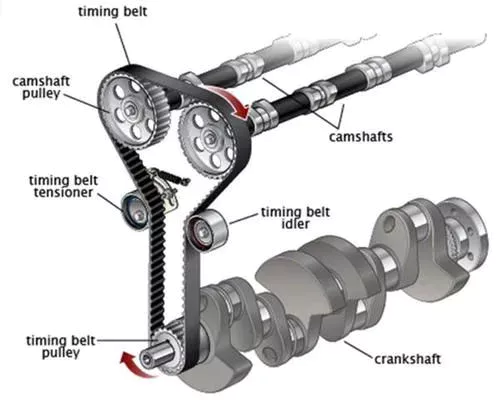
Misaligned idler pulley
If the tensioner arm is not rotating freely or has an abnormal chirping noise, it could be the result of a misaligned idler pulley. If this is the case, replace the idler. If the idler does not move, you may need to adjust the accessory mount points or use a laser alignment tool. The tensioner arm is only 1 part of the tensioner.
A misaligned idler pulley on a belt tensioner is usually the cause of a squeaking noise. If this noise continues even after a replacement of the belt, it’s time to replace the whole belt. A misaligned idler pulley can also be the cause of premature belt wear. If the idler pulley is out of alignment, it could also cause the belt to wear too fast and lead to the premature failure of the timing belt.
The tensioner pulley is made of nylon, steel, or plastic. It may be flat or grooved. Before replacing it, check for any cracks, dents, or debris on the pulley’s surface. Plastic pulleys may have broken sidewalls. If the idler pulley is worn out, you might also notice squealing noises when the vehicle is in motion.
The misalignment of a belt is most pronounced when the span between the 2 pulleys is short. When the span is long, however, diagnosing the problem becomes more complicated. Small degrees of offset may not be visible to the naked eye, but a laser alignment tool can help identify these subtle variations. In order to identify a misaligned idler pulley on a belt tensioner, you must first determine its cause.
When the tensioner’s idler pulleys are out of line, a belt tensioner will not be able to properly adjust the torque that the belt is under. This may result in squealing noises. If this is the case, it is time to call a mechanic. He or she will be able to determine the cause and correct it. If you suspect the problem, your next step is to replace the idler pulley on the belt tensioner.
If the ribbed belt is not properly aligned, you may have a misaligned idler pulley. To fix the misalignment, locate the belt adjustment bolt underneath the hood. You should be careful not to damage the alternator or battery terminal while doing this task. If you do accidentally connect the battery positive to the earth, you might be able to damage the ribbed belt and ruin your vehicle’s timing.
Besides a misaligned idler pulley on the belt tensioner, another problem may be the alternator’s serpentine belt. If your car’s alternator belt is not aligned properly, you could have misaligned the alternator’s pulley or a worn-out bearing. Regardless of the cause of your problem, you should have the belt inspected.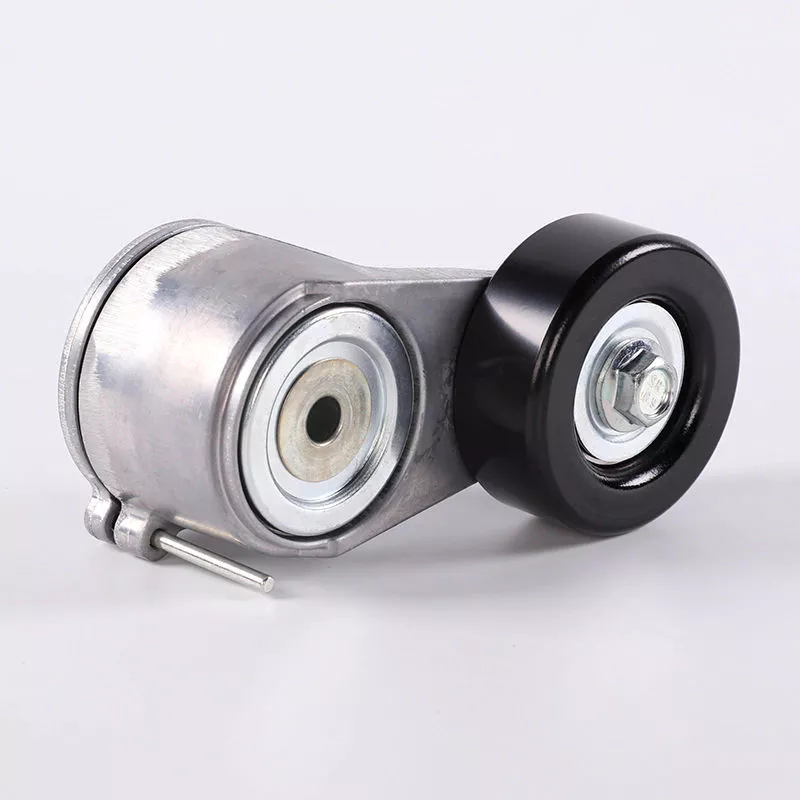
Bad idler pulley
Having a Bad Idler Pulley on a Belt Tensioner? If this sounds familiar, then it’s probably time to change it. Idler pulleys slowly take hits while the engine is running, causing the belt to wrap and bend. Eventually, the belt will slip, and a new idler pulley should be installed to ensure optimal tension. But before you spend a dime on a new one, let’s talk about what to look for.
Symptoms of a Bad Idler Pulley: If the noise persists, there is a problem with the idler pulley or its bearing. These parts wear out over time and may eventually cause a cracked idler pulley or serpentine belt. Not only will the idler pulley create an irritating noise, but it will also damage the belt itself, leading to overheating, stalled engine, and even damage the head gaskets. Thankfully, a Bad Idler Pulley on a Belt Tensioner is easily replaced and will only cost about $40.
Although the Idler Pulley is not the most popular component on a car, it’s a critical part that ensures that the engine runs smoothly. It’s easy to overlook this part, but its failure can make it impossible for your vehicle to operate at its optimal level. Moreover, a Bad Idler Pulley on a Belt Tensioner will cause your engine to malfunction, so it’s essential that you check it at regular intervals.
If you notice a squealing noise while driving, the Idler Pulley is likely the culprit. Because of friction between the engine belt and idler pulley, the engine belt rubs against the pulley, causing it to squeak and make a clicking noise. This squealing noise will continue until the problem is repaired or replaced. It’s time to start addressing the problem before it becomes too late.
If you notice the tensioner pulley moving away from the engine, it’s most likely that the pulley is malfunctioning. A belt that is loose or slack may make it difficult to start the car, or your engine may even overheat. If this occurs, it’s crucial to replace the Idler Pulley as soon as possible, because a Bad Idler Pulley on a Belt Tensioner can seriously damage your vehicle.
The Idler Pulley facilitates the motion of the engine belt. It serves as a smooth rotating point that allows the belt to loop without a barrier. Over time, this part of the system will begin to show signs of wear and tear, and replacement is vital to protect your engine, serpentine belt, and other accessories. An early warning sign of a problem is a squealing sound coming from the engine area.
Broken tensioner arm
The belt tensioner is a piece of machinery that is used to keep the belt tight. If this part breaks, you can easily repair it yourself using a long-handled ratchet, serpentine belt tool, or a socket. To repair the tensioner, simply remove the drive belt from the pulley and rotate it to release tension. Check for roughness, resistance, or binding of the drive belt.
Noises caused by the tensioner are a sign of a damaged component or excessive oscillation. These noises are usually caused by worn internal components or the tensioner’s pivot bushing. In some cases, the vibration damping system or a worn-out alternator pulley could also be to blame. If this is the case, replace the pulley and tensioner together. To check the condition of your belt tensioner, follow these steps.
In addition to worn-out springs, a loose or broken pivot arm could be causing your belt to misalign. A worn-out tensioner pulley bushing will also cause vibrations, noise, and seizing. Lastly, a broken tensioner spring could be preventing the belt from maintaining proper tension. Broken springs are also prone to loss of tension due to heat. Damaged tensioner housing can also affect belt tension.
Once the belt is installed, you need to check the condition of the pulley and the tensioner arm. Make sure that the pulley is moving and that the arm is moving smoothly with the cranking and releasing. If the arm is wobbling, the tensioner is failing. If the pulley wobbles or excessive chattering occurs, the tensioner is failing. It can also be seized or jammed.
If the tensioner arm has broken, replace it. Replacing the tensioner can be a tedious task. Be sure to use a suitable tool to tighten the pulley and tensioner. If you are not sure of how to replace the pulley, try using a serp belt tool. Another good option is to purchase a 3/8 drive ratchet. If you don’t have this tool, you can use a long 3/8 extension and a deep socket.
The belt tensioner assembly can fall off the engine, causing damage to the timing belt. If you are replacing it, you must replace it with a new one, and tighten all of the mounting bolts before reinstalling it. To avoid further damage to the engine, ensure you replace the belt with a new tensioner and a new belt. The tensioner is bolted to the engine’s timing cover, so make sure you carefully tighten the bolts when replacing it.


China Good quality Bearings for Conveyor Agricultural Machinery Diesel Hydraulic Press Excavator Spare Parts Textile Machine Engraving Machine Concrete Deep Groove Ball Bearing with Best Sales
Product Description
QUICK OVERVIEW
| Model | Deep Groove Ball Bearing |
| Greese/Oil | As your requirement, such as open, z,zz,rz, 2rz,rs, 2rs, and so on. |
| Vibration | Z1/V1,Z2/V2,Z3/V3 |
| Tolerance codes | ABEC-1, ABEC-3, ABEC-5, ABEC-7 |
| Internal clearance codes | C0, C2, C3, C4, C5 |
| Snap ring | N, NR |
| Quality level | Reach the same level as Japanese and European bearings, P0 P2 P4 P5 P6.. |
| Feature | Low voice, High speed, Low friction, long service life |
| Application | Pharmaceutical equipment, medical equipment, textile machinery and accessories, knitting machines, weaving machines, spinning equipment, textile accessories, non-woven fabric machinery, textile equipment, machinery, metal, mold, automotive electronics, electrical, instrumentation, military, aviation aerospace, plastics and rubber industry, medical and other fields. |
| Package | 1,barreled package+outer carton+pallets 2,single box+outer carton+pallets 3,tube package+middle box+outer carton+pallets 4,According to your’s requirement |
| Details | We have a complete process for production and quality assurance to make sure our products can meet your requirement. 1.Assembly 2.Windage test 3.Cleaning 4.Rotary test 5.Greasing and gland 6.Noise inspection 7.Appearance inspection 8.Rust prevention |
Deep groove ball bearings are the most representative structure in rolling bearings and have been widely used in many industries, such as cars, compressors, construction, electric motors, food industry, home appliances, etc. They are suitable for high or even extremely high-speed operation, and very durable, and need not be maintained regularly. This kind of bearing has a small friction coefficient, high limit speed. Widely used in industrial machinery, automobile, electrical system.
Application and popular suitable models:
1.Motorcycle rear wheel bearing: 63032RS, 6302 2RS
2.High-speed ball bearing for electric tools: 628ZZ, 688ZZ
3.Bearing for electric motor: 6204 2RS, 6205 2RS
4.Skateboard rubber roller bearings: 608 2RS, 6072RS, 6092RS, 6282RS
5.Stainless steel deep groove ball bearings for the food industry: S6900 2RS, S6901 2RS
6.Ceiling fan bearing: 6202 ZZ, 6203 ZZ
7.Thin wall deep groove ball for sweeper: 6900, 6800 series
Pictures
Model List (Please contact with us for more models)
| Product | Bore Dia (d) (mm) | Outer Dia (D) (mm) | Width (B) (mm) | Radius (min) (rs) (mm) | Dynamic Load Rating (Cr) (N) | Static Load Rating (Cor) (N) |
| 6000 | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 4,550 | 1,950 |
| 6000-2RS | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 4,550 | 1,950 |
| 6000ZZ | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 4,550 | 1,950 |
| 6200 | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6200-2RS | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6200ZZ | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6300-2RS | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6300ZZ | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6001-2RS | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6001ZZ | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 5,100 | 2,400 |
| 6201 | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6,800 | 3,050 |
| 6201-2RS | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6,800 | 3,050 |
| 6201ZZ | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6,800 | 3,050 |
| 6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 9,700 | 4,200 |
| 6301-2RS | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 9,700 | 4,200 |
| 6301ZZ | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 9,700 | 4,200 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 5,600 | 2,850 |
| 6002-2RS | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 5,600 | 2,850 |
| 6002ZZ | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 8,100 | 3,450 |
| 6202 | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 7,650 | 3,750 |
| 6202-2RS | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 7,650 | 3,750 |
| 6202ZZ | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 7,650 | 3,750 |
| 6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 11,400 | 5,450 |
| 6302-2RS | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 11,400 | 5,450 |
| 6302ZZ | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 11,400 | 5,450 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6,000 | 3,250 |
| 6003-2RS | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6,000 | 3,250 |
| 6003ZZ | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6,000 | 3,250 |
A wide range of applications:
• agriculture and forestry equipment
• automotive and industrial gearboxes
• automotive and truck electric components, such as alternators
• electric motors
• fluid machinery
• material handling
• power tools and household appliances
• textile machinery
• two Wheeler.
Our Bearing Advantage:
1.ISO Standard
2.Bearing Small order accepted
3.In Stock bearing
4.OEM bearing service
5.Professional:20 years manufacture bearing
6.Customized bearing, Customer’s bearing drawing or samples accepted
7.Competitive price bearing
8.TT Payment or Western Union or PayPal
Our Company
| Packaging Details | 1 piece in a single box 50 boxes in a carton 20 cartons in a pallet |
| Nearest Port | ZheJiang or HangZhou |
| Lead Time | For stock parts: 1-5 days. If no stock parts: <200 pcs: 15-30 days ≥200 pcs: to be negotiated. |
FAQ
1.How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
– We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
– We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
2.Do you test all your goods before delivery?
– Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
3.What products does your company supply?
– Auto Bearings (Wheel Bearings, Wheel Hub Bearings, Clutch Bearings, Belt Tensioners and Water Pump Bearings etc. )
-Industrial Bearings (Deep Groove Ball Bearings, Tapered Roller Bearings and Pillow Block Bearings).
How to Repair a Timing Belt Tensioner
Your timing belt tensioner is a critical component of your vehicle’s drivetrain. Too little tension, for example, will cause the belt to slip, and too much tension can overload shaft bearings, leading to premature failure. If you notice that your belt tensioner is not working properly, you should immediately visit a mechanic. Corrosion from road splash, dirt, mud, or other debris can jam the tensioner housing. To avoid this, make sure that you replace your timing belt tensioner as soon as possible.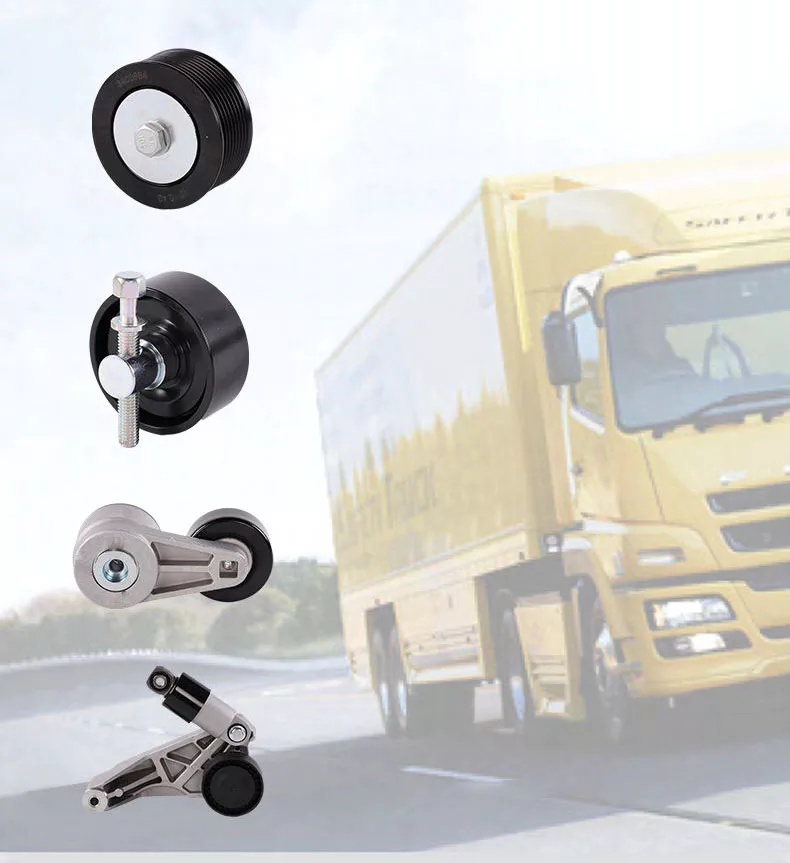
Symptoms of a bad belt tensioner
If you’ve ever wondered what signs indicate a bad belt tensioner, look no further than your vehicle’s engine. Worn belts or a broken tensioner can cause an irritating squealing noise, as well as the belt to slip. Even worse, a bad tensioner can cause water to enter the belt and pulley, resulting in water damage. A worn tensioner is usually the culprit of the noise, but there are also other warning signs that a belt is in trouble.
Your vehicle’s engine may start to run poorly or even squeal when you turn the key. Similarly, your engine may fail to start at all, or the check engine light may illuminate. The belt may also start to wear out in an unusual pattern. These signs indicate that the tensioner is in need of replacement. If you notice 1 or more of these signs, get your car checked right away.
To check the condition of the tensioner, remove the drive belt and observe the pulley. You may notice rust dripping or bleeding at the mounting bolts, which are the most common signs of a bad tensioner. If you can’t remove the drive belt, check the pulley by rotating it. If you feel resistance, the pulley is likely worn or slack.
Failure of the belt tensioner will also cause other parts of the car to fail. If a bad belt tensioner isn’t fixed quickly, you might not be able to use the vehicle properly. You could end up breaking your car’s engine, losing power steering, and possibly even the water pump. If your car is not running right, you could be stuck in the middle of nowhere. Even if the alternator doesn’t work, you’ll still have a malfunctioning power steering system and a dead AC system.
A broken timing belt tensioner can cause strange noises or a no-start condition. These noises and symptoms are signs of a bad belt tensioner, and you’ll have to replace it ASAP. If you don’t know what symptoms mean, don’t hesitate to take your car to a mechanic. You’ll be surprised how easy it is to check this vital component and save yourself a bunch of money.
Components of a belt tensioner
The components of a belt tensioner assembly consist of 4 key components. The clearance between the pulley and the base is critical to the tensioner’s operation. If the tensioner is installed incorrectly, the spring can break and cause severe injury. The spring’s preload and powerful force make it difficult to service the unit safely. These parts are non-serviceable. If you are unsure of how to repair your tensioner, contact an authorized mechanic.
The components of a belt tensioner drive are shown in FIG. 2. The rotor shaft is connected to the drive screw, while the second transmission is connected to the gear shaft. The rotor and gear shaft are in parallel with each other. The gear shaft and worm wheel are connected to the belt tensioner drive. In other words, the belt tensioner drive is located in the B-pillar of the motor vehicle.
A belt tensioner may be equipped with a drive shaft and electric motor. The drive shaft may also contain a worm gear or worm wheel. The drive shaft also has an intermediate gearbox. Once the tensioner is set, it is ready to move to its safe-position position. It is a relatively simple and inexpensive replacement for your belt. When replacing a multi-ribbed belt, be sure to replace the tensioner along with the belt. Gates recommends replacing all wear parts at once.
In the event of a faulty drive belt tensioner, the belt will not stay taut. The pulley can wobble and cause the belt to fray. In addition to this, the bearings can cause a loud squealing noise. In this case, the accessory motors will continue to run, while the belt itself will not. Therefore, replacing the timing belt tensioner is an important part of maintaining the car.
In some systems, the belt tensioner uses a worm gear as the first gear. This results in rolling engagement of the screw’s teeth. This reduces noise and vibrations, while maximizing the efficiency of the belt tensioner drive. Additionally, a worm gear can eliminate the need for additional parts in belt tensioners. While this may not be practical in all instances, it is a good choice for space-constrained environments.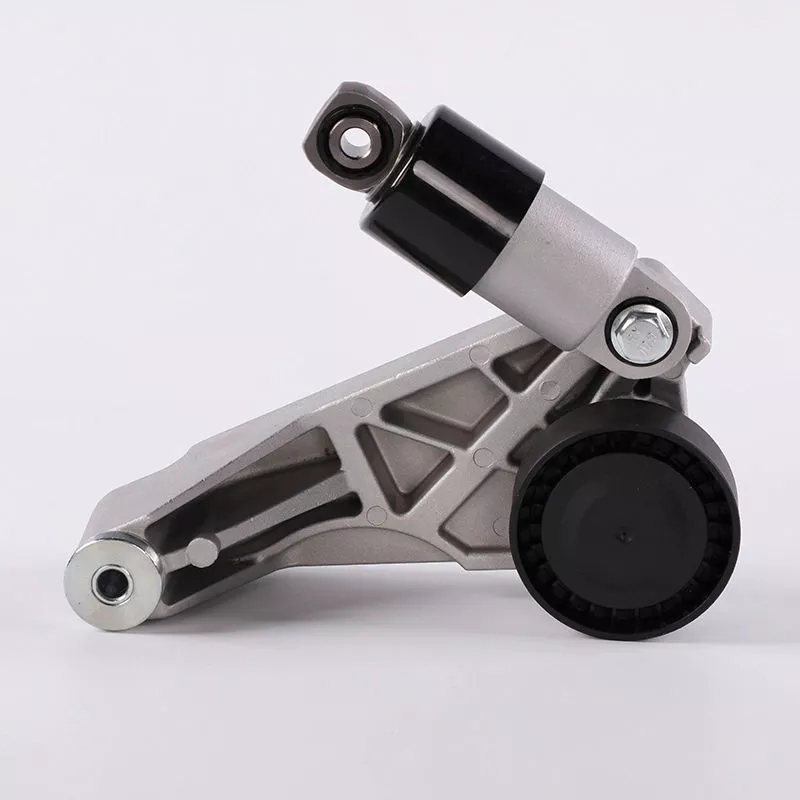
Repair options for a timing belt tensioner
A timing belt tensioner is an essential part of an automobile’s timing chain and is responsible for ensuring proper timing. Proper alignment of timing marks is essential to the proper operation of the engine, and improper alignment may lead to damage to the engine. To repair a timing belt tensioner, there are several repair options available. First, you need to remove the engine cover. You can then remove the timing belt tensioner by loosening the pulley using a ratchet or breaker bar.
When the timing belt isn’t properly tensioned, the engine will misfire. The engine misfires when the valve opens and the pistons rise at the wrong time. When this happens, the timing belt cannot properly grip the gears and the engine will not function. If this part fails, you’ll have to replace the whole timing chain. However, if you are handy with tools, you can easily replace the entire timing belt tensioner yourself.
If your timing belt tensioner is out of alignment, you should replace it. If you’re not sure whether it needs to be replaced, check it with a professional and learn the details of the repair. The timing belt tensioner is the most critical part of the engine, so it’s important to know about it. Otherwise, your car won’t run as well as it could. Repair options for a timing belt tensioner will vary depending on the severity of the problem and how much damage it has done.
While there are several repair options for a timing belt tensioner, the average cost of replacement is $364 to $457, and this doesn’t take into account any tax or fee you may be charged. DIY repair methods will usually cost you $50 to $150, and you’ll likely save a lot of money in the process. However, you need to remember that you may be unable to do the job yourself because you don’t know how to use the proper tools and equipment.
While it is not difficult to replace a timing belt tensioner on your own, you should know that you’ll need to remove other parts of the engine as well as special tools to make the repair properly. This is an advanced repair job and requires a great deal of skill. If you’re new to home car repair, you may not want to attempt it yourself. There are many other options, such as hiring a mechanic.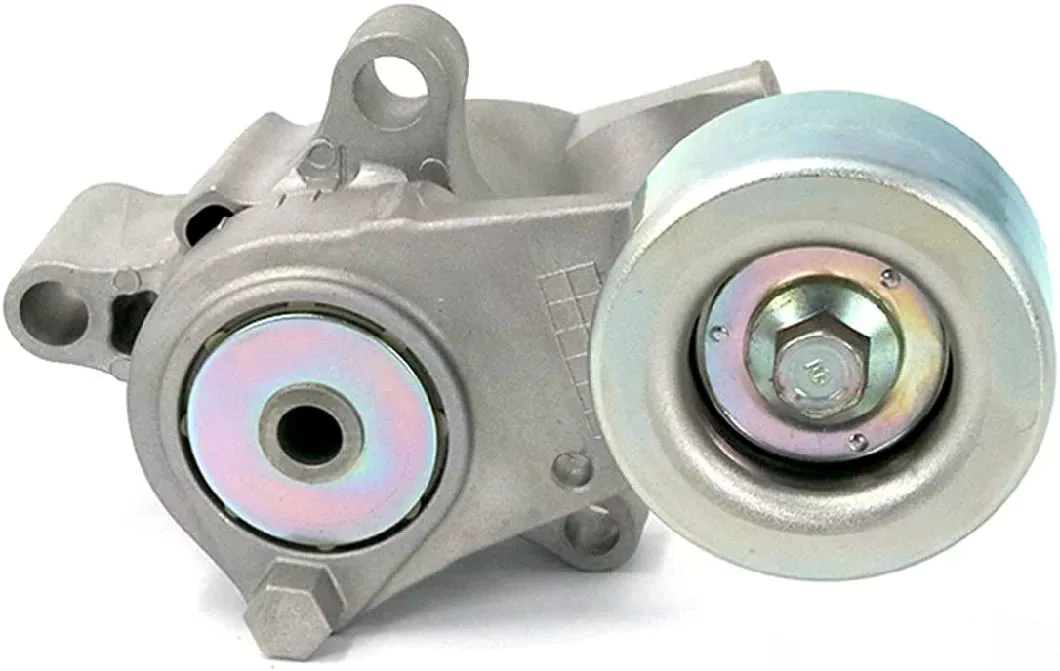
Installation instructions
While there are no universal installation instructions for belt tensioners, the manufacturer of your car may provide detailed instructions. Before attempting to replace your tensioner, read the manufacturer’s recommended procedures carefully. To install a new tensioner properly, unload the old 1 and take a picture or sketch of how the belt should be routed. Once the old tensioner is out, follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications. Make sure to unload and remove the belt from the tensioner, and follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications to install the new one.
If your car comes with a manual belt tensioner, you can follow the instructions. The manual will have a corresponding guide for installation. When installing a belt tensioner, make sure the manual clearly states the static tension for your particular model. Check that it is in line with the engine relief to ensure proper belt tension. You can then use a 6mm allen key to turn the tensioner clockwise and counterclockwise. Once it is in position, release the tensioner to operate. The belt tensioner should now apply the proper tension to your belt.
Before installing a new belt tensioner, make sure you read the manual completely. You should follow these steps carefully to avoid any problems with the tensioner. If the tensioner has failed, you must replace it immediately. A new belt tensioner will help you ensure proper performance of your accessory belt drive system. If you are installing a new multi-ribbed belt, you should replace the tensioner as well. However, it is important to note that replacing the belt tensioner is a complicated process and requires a mechanic to be able to safely remove the belt from the engine.
To install a second stage drive belt, walk the belt onto the input drive and generator. Ensure that the belt is seated properly in the grooves of the pulleys. Next, replace the input drive belt and right and left Drive Disk covers. Test the machine to ensure that it is working properly. If it doesn’t, replace the original drive belt. After installing the new belt, you may want to read the manual again to make sure it is in perfect condition.

