Product Description
| Product Name.: | tensioner |
| Part No.: | 3945527 |
| Quality.: | proper mass |
| Trademark.: | DFYAHAN or Customized |
| Delivery Time.: | Quick delivery |
| MOQ.: | 1 PCS |
| Service.: | Best aftersale service |
| Weight. : | 2Kg |
1, International Express.Such as DHL, UPS, EMS, ARAMEX and so on.Usually after 5 to 7 days
you can get the packages.
2, Air Transportatio:.For goods above 100kg, it is a economical choice for the customers.
3, International Marine Container.
1, We will send the goods as fast as we can to save your time..
2, All the pictures on our website are real images of the part itself, what you see is what you get.
3, Goods will Be packed safe & carefully
1. Genuine parts or OEM partsor aftermarket parts are both available.
2.Products are in best quanlity and best price.
3. Warranty is SIX months.
4. For mass order, package can be customized.
ShiYan YAZHAN Exhibition is located in HangZhou, ZheJiang , the capital of trucks in China (the birthplace of Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Motors). The company adheres to the principle of never giving up once cooperation, CZPT operation, and customer first to provide the best service to new and old customers.
The company’s product range includes Cumminss B, C, L, LK series mechanical diesel engines, ISB, ISDe, QSB, ISLe, ISL, QSL, ISZ, QSZ and other electronic controlled diesel engines, as well as B, C, L series natural gas engines. The engine displacement includes 2.8L, 3.8L, 3.9L, 4.5L, 5.9L, 6.7L, 8.3L, 8.9L, 9.5L, and 13L, with a power coverage range of 80-680 horsepower;
Including: 1. Cumminss engine assembly
2. Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Cumminss engine accessories (B3.3/4B3.9/6B5.9/6C8.3/6L8.9/ISBe/ISCe/ISDe/ISLe)
3. ZheJiang Cumminss Engine Accessories (Nt855/Kta19/Kta38/Kta50/QSK23/QST30)
4. HangZhou Cumminss Engine Accessories (ISM/QSM)
5. CZPT Cumminss engine accessories (ISF2.8/ISF3.8/ISG)
6. Frega filter
7. Boschs fuel injectors, fuel pumps, and other series
8. Engine aftertreatment urea pump series
Question 1:How to buy engine spare parts? First of all, please tell us the part number of the parts you need. We will supply the same parts as yours. Secondly, if you don’t know the part number, please provide parts name and engine series number, then we will check the part number through engine series number.
Question 2:How long is the delivery time? For complete engine and Power units , we need to arrange production according to the order, our general delivery time is 15-30 days. For spare parts , our general delivery time is 3-10 days.
Question 3:How to arrange delivery? Considering the large volume and weight of our products, to save the shipping cost, we generally recommend ship to your nearest port For small items and urgent orders, we can also provide air shipment and send goods to the airport in your city or your company address.
Question 4:How about Payment Methods? We suggest 30/70,T/T payment method: 30 percent down payment on placement of the order, with the remaining 70% due upon shipment. Question 5:How about Packing Methods? Normally we use wooden boxes for packaging or we can pack it according to your special needs.
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

What is the role of belt tensioner materials and coatings in performance and longevity?
Belt tensioner materials and coatings play a crucial role in the performance and longevity of belt tensioners. The choice of materials and coatings directly impacts the tensioner’s ability to withstand the forces and loads encountered in belt-driven systems, resist wear and corrosion, and maintain consistent performance over time. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of belt tensioner materials and coatings in performance and longevity:
- Strength and Durability:
- Wear Resistance:
- Corrosion Resistance:
- Friction Reduction:
- Temperature Stability:
- Lubrication Enhancement:
- Noise and Vibration Damping:
The materials used in belt tensioners need to possess high strength and durability to withstand the mechanical stresses and loads imposed on them. Tensioner components are subjected to continuous movement and contact with the belt, which can lead to wear, fatigue, and potential failure. High-strength materials, such as hardened steels or alloys, are commonly used to ensure the tensioner’s structural integrity and longevity.
Belt tensioners are exposed to friction and wear as they come into contact with the belt during operation. Materials with excellent wear resistance properties, such as hardened surfaces or wear-resistant coatings, are employed to minimize the wear rate and extend the tensioner’s lifespan. These materials and coatings help maintain optimal contact between the tensioner and the belt, reducing the risk of belt slippage and premature failure.
In certain environments, belt tensioners may be exposed to corrosive substances, moisture, or contaminants, which can lead to corrosion and degradation of the tensioner components. Corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys, are often utilized to protect the tensioner against corrosive elements. Additionally, coatings like zinc plating or other protective finishes can be applied to enhance the tensioner’s corrosion resistance.
Reducing friction between the tensioner and the belt is essential for minimizing wear and maintaining consistent tension. Materials or coatings with low friction coefficients can help reduce the frictional forces and energy losses associated with the tensioner’s operation. By reducing friction, these materials and coatings contribute to improved efficiency, reduced heat generation, and increased longevity of the tensioner and the entire belt-driven system.
Belt tensioners are exposed to a wide range of operating temperatures, including both high and low extremes. Materials with good temperature stability and resistance to thermal degradation are essential for reliable tensioner performance. Heat-resistant alloys, high-temperature plastics, or thermal barrier coatings may be utilized to ensure that the tensioner maintains its mechanical properties and functionality under elevated temperatures.
Some tensioner materials or coatings are designed to enhance lubrication and reduce friction between moving parts. They may have self-lubricating properties or be compatible with specific lubricants used in the belt-driven system. These materials and coatings help reduce wear, heat generation, and the need for external lubrication, contributing to improved performance and extended longevity of the tensioner.
Belt tensioners can generate noise and vibration during operation, which can affect the comfort and performance of the belt-driven system. Certain materials or coatings can help dampen vibrations and reduce noise levels, improving the overall system’s performance and minimizing potential issues associated with excessive noise or vibrations.
In summary, the choice of belt tensioner materials and coatings is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Materials with high strength and durability, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, friction reduction, temperature stability, lubrication enhancement, and noise/vibration damping properties contribute to the tensioner’s ability to withstand the operational demands of belt-driven systems. By selecting appropriate materials and coatings, manufacturers can enhance the reliability, durability, and overall efficiency of belt tensioners, leading to extended service life and improved performance of the belt-driven systems they are used in.

How do innovations and advancements in belt tensioner technology impact their use?
Innovations and advancements in belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use, enhancing performance, reliability, and versatility. These advancements introduce new features, improve functionality, and address specific challenges associated with belt-driven systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how innovations and advancements in belt tensioner technology impact their use:
- Improved Tensioning Mechanisms:
- Enhanced Durability:
- Increased Compatibility:
- Noise and Vibration Reduction:
- Advanced Monitoring and Diagnostic Capabilities:
- Integration with System Controls:
New tensioning mechanisms and designs have been developed to provide more precise and efficient tension control. Innovations such as automatic tensioners or self-adjusting tensioners utilize advanced mechanisms that can continuously monitor and adjust the tension in real-time. This improves the overall performance and reliability of belt-driven systems, as the tension can be accurately maintained even under varying loads and operating conditions.
Advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have contributed to the development of more durable belt tensioners. High-strength alloys, advanced polymers, and specialized coatings are used to increase the resistance to wear, corrosion, and fatigue. These improvements extend the service life of belt tensioners, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement and improving the overall reliability of belt-driven systems.
Innovations in belt tensioner technology have led to increased compatibility with a wide range of belt drive systems. Manufacturers have developed adjustable tensioners that can accommodate different belt widths, profiles, and types. This versatility allows for easier integration and replacement of tensioners in various industrial or automotive applications, reducing the need for custom solutions and simplifying maintenance and repairs.
New technologies and designs have been introduced to minimize noise and vibration generated by belt tensioners. Innovative damping materials, improved bearing systems, and optimized geometries help reduce noise and vibration levels, resulting in quieter and smoother operation. This is particularly beneficial in applications where noise reduction and operator comfort are essential.
Advancements in belt tensioner technology have facilitated the integration of monitoring and diagnostic capabilities. Smart tensioners equipped with sensors and connectivity features can provide real-time data on tension levels, temperature, and other operating parameters. This enables predictive maintenance, early fault detection, and optimized performance. By leveraging data-driven insights, operators can make informed decisions, improve system efficiency, and prevent unexpected failures.
Innovative belt tensioner technologies can be integrated with system controls and automation platforms. This allows for seamless integration into larger control systems, enabling automated tension adjustments, synchronization with other components, and coordinated operation. The integration of belt tensioners with system controls enhances system performance, efficiency, and overall productivity.
In summary, innovations and advancements in belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use. These advancements improve tensioning mechanisms, enhance durability, increase compatibility, reduce noise and vibration, enable advanced monitoring and diagnostics, and facilitate integration with system controls. By incorporating these innovations, belt tensioners offer improved performance, reliability, and versatility, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements in various industrial and automotive applications.

What industries and machinery commonly use belt tensioners for optimal belt performance?
Various industries and machinery rely on belt tensioners to achieve optimal belt performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries and machinery that commonly use belt tensioners:
- Automotive Industry:
- Industrial Machinery:
- Power Generation:
- Agricultural Equipment:
- Construction and Mining:
- HVAC and Refrigeration:
The automotive industry extensively utilizes belt tensioners in vehicles for various applications. Belt tensioners are commonly found in the engine accessory drive system, where they maintain the proper tension in the serpentine or V-belts that power components such as the alternator, air conditioning compressor, power steering pump, and water pump. Belt tensioners ensure efficient power transmission, reduce belt slippage, and contribute to the overall reliability and performance of automotive engines.
A wide range of industrial machinery relies on belt tensioners for optimal belt performance. Industries such as manufacturing, food processing, packaging, printing, and material handling use belt-driven systems for conveyor belts, production lines, pumps, compressors, and other equipment. Belt tensioners help maintain the proper tension in these applications, ensuring smooth operation, efficient power transmission, and minimizing downtime due to belt slippage or failure.
In the power generation sector, belt tensioners are commonly used in applications such as generators, turbines, and auxiliary equipment. These systems often utilize belts to transfer power between components, and the tensioners play a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension. Belt tensioners help optimize power transmission efficiency, reduce vibrations, and enhance the overall reliability of the power generation equipment.
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and other farming equipment, often rely on belt-driven systems for various operations. Belt tensioners are utilized to maintain the tension in belts powering agricultural implements, such as harvesters, balers, and grain conveyors. By ensuring optimal tension, belt tensioners contribute to the efficient operation of agricultural equipment, improving productivity and reducing maintenance requirements.
Construction and mining industries commonly employ belt-driven systems in equipment such as excavators, loaders, crushers, and conveyor systems. Belt tensioners are used to maintain the proper tension in belts powering these machines, ensuring reliable and efficient operation in demanding environments. Belt tensioners help prevent belt slippage, reduce downtime, and contribute to the longevity of the equipment.
The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on belt-driven systems for various applications, including fans, blowers, compressors, and pumps. Belt tensioners are critical in maintaining the proper tension in these systems, ensuring efficient power transmission and reducing belt-related issues such as slippage or premature wear. Belt tensioners contribute to the overall performance and reliability of HVAC and refrigeration equipment.
In addition to the industries mentioned above, belt tensioners are also utilized in a wide range of other machinery and equipment, including woodworking machinery, textile machinery, marine propulsion systems, and more. The versatility and benefits of belt tensioners make them a valuable component for achieving optimal belt performance in numerous industrial and mechanical applications.


editor by lmc 2024-11-12
China supplier 3116 3126 3306 Engine Cylinder Block with Hot selling
Product Description
ENGINE CYLINDER BLOCK AND PARTS
PARTS RANGE :
Cylinder block, cylinder head ,main bearing , crankshaft, piston,liner, camshaft, Rod, oil cooler, water radiator, oil pan, oil pump, fuel pump, water pump, turbocharger, fan ,belt, injector, alternator, flywheel, starting motor
FIT ENGINE:
CUM MINS: NT855-C280, NT855-C360, NT855-C4) Harness-ECM wiring
457110 (: 2864514) Harness-ECM wiring
4955706 (: 4972857) Water pump
2864571 (CPL-2828) Cylinder head assy
4952832 (CPL-8545) Cylinder head assy
21Q6-41000 ( ) Alternator
4903472 (CPL-8545) Injector (QSM11)
4026222 (CPL-2828) Injector (QSM11)
3411754 Injector (ISM11)
2.430-00171 COVER
2.180-00070 GASKET
2.410-00060 CYLINDER BLOCK SUB ASS`Y
2.430-00121 . CAP;SEALING
2.120-00173 . BOLT;BEARING CAP
2.430-00122 . CAP;SEALING
– . CAP ASS`Y
2.181-00441 PLUG;TAPER
2.123-00146 PIN;DOWEL
2.405-00145 SHAFT;IDLER
2.429-00044 XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.;OIL LEVEL
2.123-00147 PIN;DOWEL
2.181-00361 PLUG;EXPANSION
2.408-00114 BUSHING;KNOCK
2.408-00115 BUSHING;KNOCK
2.408-00116 BUSHING;KNOCK
A218070 BUSHING
2.181-00442 PLUG;TAPER
2.180-0 0571 SEAL;SIDE
2.412-00163 PLATE;FRONT W/O PTO
2.423-00065 CASE;OIL SEAL
2.180-00140 GASKET;FRONT PLATE
2.180-00170 GASKET;OIL SEAL CASE
2.180- 1 SEAL;OIL REAR
2.405-00157 SHAFT;OIL FILTER
2.181-00443 PLUG;TAPER
2.120-00085 BOLT
2.120-0 0571 BOLT;WITH WASHER
2.120-0571 BOLT;WITH WASHER
2.177-00018 METAL SET;CRANK SHAFT
2.177-00019 METAL SET;CRANK SHAFT 0.25
2.177-0571 METAL SET;CRANK SHAFT 0.50
2.402-05717 HOUSING;FLYWHEEL
A218347 BOLT;WITH WASHER
2.181-00193 PLUG
2.120-0 BOLT
2.119-00007 GAUGE;OIL LEVEL
2.150-00009 HANGER;ENGINE
2.423-00037 CYLINDER HEAD ASS`Y
2.430-00121 . CAP;SEALING
2.430-00124 . CAP;SEALING
2.429-00064 . XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.;VALVE
2.180-00127 GASKET;CYLINDER HEAD
2.120-5714 BOLT;CYLINDER HEAD
2.120-05711 BOLT;FLANGE
2.120-0 0571 BOLT;WITH WASHER
2.181-00445 PLUG;TAPER
2.430-0 0571 CYL. HEAD COVER ASS`Y
– “. PIPE,COOLING”
2.180-00072 . GASKET
– . COVER;CYL. HEAD
2.121-00119 NUT;CAP
2.114-57170 WASHER;PLAIN
2.184-00012 HOSE;BREATHER
2.430-00082 CAP;FILLER
2.409-00149 PISTON STD 18mm
30L17-1571 “PISTON,STD;21 mm PIN”
2.409-00119 PISTON 0.25
2.409-00120 PISTON 0.50
2.115-00171 RING SET;PISTON STD
2.115-00169 RING SET;PISTON 0.25
2.115-00170 RING SET;PISTON 0.50
2.428-00033 CONNECTING ROD ASS`Y 18mm
30L19-00031 “ROD,CONNECTING;21mm”
2.121-00040 . NUT
2.120-00184 . BOLT;CONNECTING
– . ROD;CONNECTING
– . CAP;CONNECTING
2.177-00017 METAL SET;CON-ROD STD
2.177-00015 METAL SET;CON-ROD 0.25
2.177-00016 METAL SET;CON-ROD 0.50
2.405-00092 SHAFT;CRANK
2.105-00012 PULLEY;CRANK SHAFT
2.403-00091 GEAR;CRANK SHAFT
2.121-00154 NUT;JAM
2.114-57171 WASHER;PLAIN
2.114-01115 WASHER;SPRING
2.113-00016 KEY;WOODRUFF
2.154-00007 FLYWHEEL ASS`Y
2.403-05719 . GEAR;RING
– . FLYWHEEL
2.120-05717 BOLT;FLYWHEEL
2.430-00137 CAP;VALVE STEM
2.405-00173 ROCKER SHAFT ASS`Y
2.121-00155 NUT;JAM
2.115-0571 RING;SNAP
2.131-0571 SPRING;ROCKER SHAFT
2.145-00003 STAY;ROCKER
2.123-00156 PIN;GROOVED
2.310-00006 ARM;ROCKER
2.120-00521 SCREW;ADJUSTING
2.421-00169 VALVE;INTAKE
2.421-00154 VALVE;EXHAUST
2.131-00489 SPRING;VALVE
2.115-00077 RETAINER;VALVE
2.421-00172 VALVE;LOCK STEM
2.180-0 0571 SEAL;VALVE STEM
2.120-5711 BOLT;ROCKER STAY
2.429-00128 TAPPET
2.428-00049 ROD;PUSH
2.120-00091 BOLT
A218132 WASHER;SPRING
2.114-57172 WASHER;PLAIN
2.114-0 0571 WASHER;CAM SHAFT STOP
2.109-00115 BEARING;BALL
2.405-00080 SHAFT;CAM
2.403-0 GEAR;CAM SHART
2.113-00016 KEY;WOODRUFF
2.120-00090 BOLT;WITH WASHER
2.412-00142 PLATE;DISTANCE
2.113-00015 KEY;SUNK
2.109-00116 BEARING;BALL
2.403-00135 GEAR;FUEL INJ PUMP
2.115-571 RING;SNAP
2.405-00127 SHAFT;FUEL INJ PUMP
2.403-00148 IDLER GEAR ASS`Y
2.115-0571 RING;SNAP
2.415-00003 NOZZLE & HOLDER ASS`Y
2.180-00148 GASKET;HOLDER
2.140-00013 PIPE ASS`Y
2.140-00014 PIPE ASS`Y
2.140-00015 PIPE ASS`Y
2.140-00060 PIPE;FUEL RETURN
2.121-00041 NUT
2.180-00142 GASKET;FUEL RETURN
2.140-00051 FUEL PIPE ASS`Y
2.138-00004 . JOINT
2.184-00014 . HOSE;FUEL
2.184-00002 . HOSE
2.124-00037 . CLIP
2.241-00035 FUEL PUMP ASS`Y
2.198-00002 . MOUNT;RUBBER
What Is a V-Belt?
A v-belt is a type of belt that provides a continuous motion to the vehicle’s wheels. This type of belt is made of several different components. They usually have a trapezium-shaped cross-section because of its elastomer core. Elastomers are often made of polyurethane or a synthetic rubber with good shock resistance. Sometimes, a v-belt will have 2 sections – cushion rubber and compression rubber.
Link-type V-belt
A laminated link-type V-belt is 1 embodiment of the present invention. The belt comprises individual lamina sections connected longitudinally by studs and tubes, each of which has at least 1 connecting means. The slots in the links allow for a full share of the load to be transferred through the belt, and they also reduce substantially all internal mechanical stresses. The belt is preferably designed to extend substantially the entire width of the machine being driven.
Conventional link-type V-belts are installed between 2 pulleys on the tight side of the V-drive. A wide end of a link moves in the direction of rotation, while the stud of a second, smaller link pulls the nose end of the third link forward. The shank of the stud pivots on a solid fabric located in hole 2 of the third link below. The bottom link, however, curls over the stud and the belt is assembled.
The present invention offers an improved method of forming a link-type V-belt. The belt is manufactured using links and does not have to be fitted as tightly as conventional link-type V-belts. This belt is flexible and strong enough to handle normal tension loads in a well-designed drive. In addition, the belts made using the present invention will have a longer life, thereby extending the drive’s load-carrying capacity.
Classical V-belt
A classical trapezoidal belt profile makes the VB Classical V-belt ideal for various industrial applications. Available in small sizes from 5mm to 3mm, these belts are available with cogged or raw edges. Their highly engineered construction makes them ideal for a variety of uses. These belts are commonly used in motors, compressors, milling machines, mixers, and other mechanical devices. To determine the right belt for your application, consider the following factors.
The classic v-belt is the most common and economically-priced type of v-belt. They are manufactured using special formulated rubber reinforced with polyester cords. These belts can span from 16 inches to 400 inches in length. The classic V-belt is also very easy to replace. The belt’s outer diameter and pitch can be measured. The length is typically standardized by the Association for Rubber Product Manufacturers.
Typically, classical V-belts are used in single-belt drives. Because they don’t require lubrication or maintenance, these belts are often available in sizes A and B. However, larger belt sizes are rarely used for single-belt drives. In such cases, multiple A or B belts are an economical alternative to single-belt C. In addition, narrower-profile V-belts provide higher power ratings than conventional V-belts because of their higher depth-to-width ratio. These belts are ideal for heavy-duty applications.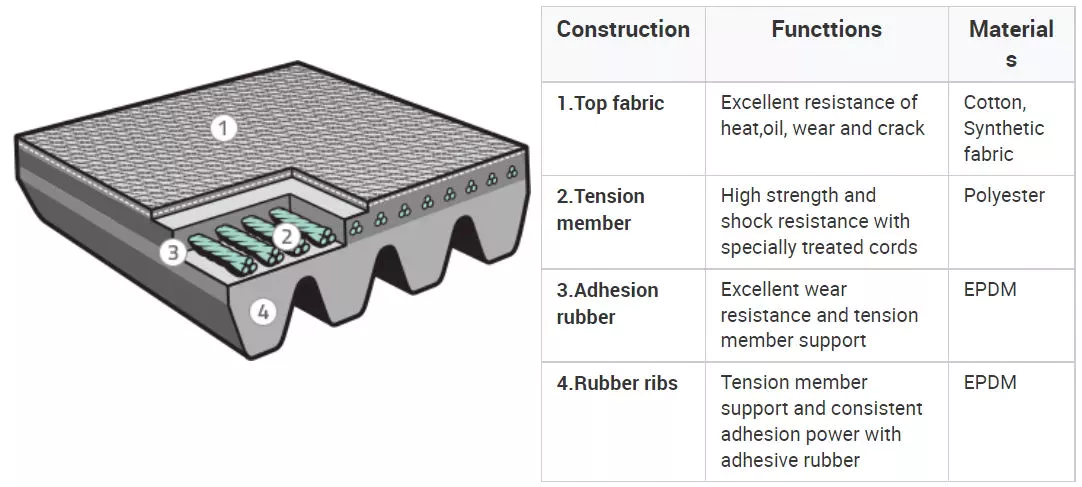
Narrow V-belt
The narrow v-belt is the same as a conventional v-belt, but it has a smaller top and bottom width. This makes it suitable for higher horsepower applications, and it is used in high-end sports cars. Narrow v-belts are generally characterized by a letter “v” on the top side and a length of outside dimensions of 1.6:1.
The steel wires that comprise the core of the v-belt are endless and are free of joints. This provides the strength required for torque transmission. A base rubber compound is placed around the steel wire and acts as a medium of compression and shock absorption during power transmission. A plastic layer acts as a protective cover, and provides the rubber with a degree of temperature tolerance. While choosing a narrow v-belt, it is important to keep in mind that there are some disadvantages to a narrow V-belt.
For example, a narrow V-belt is suitable for high-power applications, and may be used in a small assembly space. Its narrow profile also allows it to be space-saving in layout and allows high-speed drives without additional belts. Furthermore, it reduces operating and maintenance costs. It is ideal for applications where space is limited, and a high torque is required. The benefits of a narrow V-belt are plentiful.
Banded belt
Identifying a banded v-belt can be tricky, but there are a few signs that can indicate a possible problem. Cracked belts can be difficult to spot, but they can be an early indicator of a more serious problem. Look for cracked underside edges, worn covers, and misplaced slack. If 1 or more of these factors applies to your belt, you may want to seek a replacement.
Banded v-belts are made with an elastomer core. The main component of this belt is the elastomer, which is used for the band’s flexural strength and shock resistance. It’s sometimes separated into 2 sections, with each section connected to the other by a tension cord. This gives the belt its trapezium cross-section, which increases tensile strength.
The 2 main types of banded v-belts are wrapped or raw edge. Wrapped v-belts have a fiber-covered body while raw edge belts are uncovered. Banded v-belts are often classified by their cross-section, and include: standard v-belt, wedge v-belt, narrow versus double v-belt, cogged v-belt, and double t-belt.
Banded v-belts are popular with commercial applications. Whether you’re looking for a 2V-belt or a large 8V-belt, V-Belt Guys has what you need. We also stock a wide variety of different banded v-belts and can help you find 1 that fits your needs and budget. Take a look at our selection today!
Traditional V-belt
Although a traditional V-belt may be a glorified rubber band, modern variations reflect advances in engineering. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for trouble-free service. When you are replacing a traditional V-belt, be sure to follow these simple steps to ensure its longevity. Read on to learn more. Listed below are the features of each type of V-belt. Identify the type of belt you need by measuring its top width, circumference, and dimensions.
TEC Traditional V-belts have an exceptionally low slip rate and are resistant to high operating temperatures. These types of belts do not experience early belt aging. They are also highly resistant to poor operating conditions. However, the maintenance is more extensive than other types of belts. A typical V-belt part number is B50, which is the cross-section size of a 50-inch belt. The belt’s lifespan is greatly increased because of this feature.
A ribbed V-belt is another option. It has a deeper V than a traditional V-belt. The ribs in this type are narrower and more flexible. These ribs are smaller than the classic V-belt, but they can transmit 3 times as much horsepower. Because they are thinner, these belts are more flexible than traditional V-belts. The thickness of the ribs is less critical.
Metric V-belt
Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.
Metric V-belts are generally more durable than their equivalents made of standard American-sized belts. Metric V-belts are available in many different sizes to fit different machineries. In addition to offering superior load-carrying capacity, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are known for their exceptional flex and stretch characteristics. For optimum performance in textile mills, food processing, and machine tool applications, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are manufactured using a proprietary construction that combines a higher load-carrying capacity with superior flex and stretch.
Metric belts can generate 50% to 100% more horsepower than conventional and classic sectioned belts. This is achieved through improved construction and placement of the cord line. These belts also have unique wedge designs that help them support the cord in motion. However, you must ensure the proper tension when buying a Metric V-belt, because improper tension may damage the belt. They are compatible with both U.S. and international standards.


China high quality CZPT Wd615 Engine Parts Cylinder Head Gasket 612600040355 near me manufacturer
Product Description
CZPT WD615 Engine parts Cylinder Head Gasket 6126
Company introduction: The company is located in HangZhou, a beautiful spring city, which is the hometown of China’s heavy-duty CZPT trucks. We are professionally qualified and mainly deal in Chinese truck parts, engine parts, chassis parts, gearbox parts, and cabs. Parts, air-conditioning parts, suitable models include SINOTUCK, HOWO, XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.FENG, CAMC, SANY, HINO700, BEIBENG, JAC, WEICHAI, YUCHAI, CZPT MIXER TRUCK, HINO PC11, etc.
You are welcome to consult and inquire
KEY SERCH: CNHTC,JAC, HOWOTRUCK,HOWO DUMP TRUCK,CHINA TRUCK,HOWO,WEICHIA,SHACMAN,YUCHAI,DONFENG
WHASAPPP: 17686651489
WELCOME YOU!@
FAQ
Q1What is your terms of packing?
A:Generally,we pack our geods in Cartn boxes and then in wooden case.
Q2.What is your terms of pyment?
A: T/T, LC accept
Q3.What is your terms of delivery? A: EXW, FOB, CIE, DAF etc
Q4. How about your delivery time?A:Generally,it will take 3 to 7 days after receiving your advance payment.The specifie delivery time dependsity of your order.
Q5.Can you produce according to the samples?
A:Yes,we can produce by your smples or technical drawing.We build the molds and fixtures.
Q6.What is your sample policy?
A:We can supply the sampel if we have ready parts in stock but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
Q7Do you test all your goods before delivery? A:Yes,we have 100% test before delivery
Q8:How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customernefits
Our company specializes in pure CZPT engine parts and assemblies
Main business:
DCEC Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng engine series models 4BT3.3, 4BT3.9, 6BT5.9, 6CT8.3, 6L8.9, ISBe, ISDe, ISCe, ISLe L9.3, L9.5
DCI11 Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng engine series model Dci11
GCIC ZheJiang engine series models L9.3, L9.5
Foton engine series models ISF2.8, ISF3.8, ISG
XCEC engine series models L10, M11, ISM11, QSM11
CCEC ZheJiang engine series models NT855, N14, L10, M11, KTA19, KTA38, KTA50
A1400, A1700, A2300, NH250, NH220, VTA28, B3.3, QSB3.3, QSB5.9, QSB6.7, QSC8.3, QSL8.9, QSK19, QSK23, QSK38, QSK45 , QSK50, QSK60, QSK78, ISBE, ISCE, ISLE, QSL, L10, QSM11, ISX15, QSX15, QST30G1, QST30G2
construction machinery, generator sets, bus series models ISBE, ISCE, ISLE, QSB5.9, QSB6.7, QSC8.3, QSL8.9, QSM11, ISX15, QSX15, QST30
KOMATSU engine series models 4D95, 4D102, 6D102, 6D107, 6D114E, 6D125, 6D155, 6D170
series models C6.4, C7, C9, C10, C12, C15, C16, C18, C30, C32, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9
Products mainly include: cylinder block, cylinder head, cylinder liner, cylinder gasket, valve, valve rocker arm, piston, piston ring, piston pin, oil pump, oil pump, oil pump, water pump, oil nozzle, oil pan, camshaft, crankshaft , Connecting rod, tappet body, push rod, crankshaft bush, connecting rod bush, gear chamber and cover, engine gear, generator, starter, electronic control unit, electronic control module, air compressor, supercharger, filter , Air filter, oil cooler, intercooler, thermostat, water tank, fan belt, fan bracket, fan pulley, belt and tensioner, bushing, whole vehicle oil seal, gasket, repair kit, duct, seat Rings, cleats, bolts, washers, suspension pads, etc.
How to Repair a Timing Belt Tensioner
Your timing belt tensioner is a critical component of your vehicle’s drivetrain. Too little tension, for example, will cause the belt to slip, and too much tension can overload shaft bearings, leading to premature failure. If you notice that your belt tensioner is not working properly, you should immediately visit a mechanic. Corrosion from road splash, dirt, mud, or other debris can jam the tensioner housing. To avoid this, make sure that you replace your timing belt tensioner as soon as possible.
Symptoms of a bad belt tensioner
If you’ve ever wondered what signs indicate a bad belt tensioner, look no further than your vehicle’s engine. Worn belts or a broken tensioner can cause an irritating squealing noise, as well as the belt to slip. Even worse, a bad tensioner can cause water to enter the belt and pulley, resulting in water damage. A worn tensioner is usually the culprit of the noise, but there are also other warning signs that a belt is in trouble.
Your vehicle’s engine may start to run poorly or even squeal when you turn the key. Similarly, your engine may fail to start at all, or the check engine light may illuminate. The belt may also start to wear out in an unusual pattern. These signs indicate that the tensioner is in need of replacement. If you notice 1 or more of these signs, get your car checked right away.
To check the condition of the tensioner, remove the drive belt and observe the pulley. You may notice rust dripping or bleeding at the mounting bolts, which are the most common signs of a bad tensioner. If you can’t remove the drive belt, check the pulley by rotating it. If you feel resistance, the pulley is likely worn or slack.
Failure of the belt tensioner will also cause other parts of the car to fail. If a bad belt tensioner isn’t fixed quickly, you might not be able to use the vehicle properly. You could end up breaking your car’s engine, losing power steering, and possibly even the water pump. If your car is not running right, you could be stuck in the middle of nowhere. Even if the alternator doesn’t work, you’ll still have a malfunctioning power steering system and a dead AC system.
A broken timing belt tensioner can cause strange noises or a no-start condition. These noises and symptoms are signs of a bad belt tensioner, and you’ll have to replace it ASAP. If you don’t know what symptoms mean, don’t hesitate to take your car to a mechanic. You’ll be surprised how easy it is to check this vital component and save yourself a bunch of money.
Components of a belt tensioner
The components of a belt tensioner assembly consist of 4 key components. The clearance between the pulley and the base is critical to the tensioner’s operation. If the tensioner is installed incorrectly, the spring can break and cause severe injury. The spring’s preload and powerful force make it difficult to service the unit safely. These parts are non-serviceable. If you are unsure of how to repair your tensioner, contact an authorized mechanic.
The components of a belt tensioner drive are shown in FIG. 2. The rotor shaft is connected to the drive screw, while the second transmission is connected to the gear shaft. The rotor and gear shaft are in parallel with each other. The gear shaft and worm wheel are connected to the belt tensioner drive. In other words, the belt tensioner drive is located in the B-pillar of the motor vehicle.
A belt tensioner may be equipped with a drive shaft and electric motor. The drive shaft may also contain a worm gear or worm wheel. The drive shaft also has an intermediate gearbox. Once the tensioner is set, it is ready to move to its safe-position position. It is a relatively simple and inexpensive replacement for your belt. When replacing a multi-ribbed belt, be sure to replace the tensioner along with the belt. Gates recommends replacing all wear parts at once.
In the event of a faulty drive belt tensioner, the belt will not stay taut. The pulley can wobble and cause the belt to fray. In addition to this, the bearings can cause a loud squealing noise. In this case, the accessory motors will continue to run, while the belt itself will not. Therefore, replacing the timing belt tensioner is an important part of maintaining the car.
In some systems, the belt tensioner uses a worm gear as the first gear. This results in rolling engagement of the screw’s teeth. This reduces noise and vibrations, while maximizing the efficiency of the belt tensioner drive. Additionally, a worm gear can eliminate the need for additional parts in belt tensioners. While this may not be practical in all instances, it is a good choice for space-constrained environments.
Repair options for a timing belt tensioner
A timing belt tensioner is an essential part of an automobile’s timing chain and is responsible for ensuring proper timing. Proper alignment of timing marks is essential to the proper operation of the engine, and improper alignment may lead to damage to the engine. To repair a timing belt tensioner, there are several repair options available. First, you need to remove the engine cover. You can then remove the timing belt tensioner by loosening the pulley using a ratchet or breaker bar.
When the timing belt isn’t properly tensioned, the engine will misfire. The engine misfires when the valve opens and the pistons rise at the wrong time. When this happens, the timing belt cannot properly grip the gears and the engine will not function. If this part fails, you’ll have to replace the whole timing chain. However, if you are handy with tools, you can easily replace the entire timing belt tensioner yourself.
If your timing belt tensioner is out of alignment, you should replace it. If you’re not sure whether it needs to be replaced, check it with a professional and learn the details of the repair. The timing belt tensioner is the most critical part of the engine, so it’s important to know about it. Otherwise, your car won’t run as well as it could. Repair options for a timing belt tensioner will vary depending on the severity of the problem and how much damage it has done.
While there are several repair options for a timing belt tensioner, the average cost of replacement is $364 to $457, and this doesn’t take into account any tax or fee you may be charged. DIY repair methods will usually cost you $50 to $150, and you’ll likely save a lot of money in the process. However, you need to remember that you may be unable to do the job yourself because you don’t know how to use the proper tools and equipment.
While it is not difficult to replace a timing belt tensioner on your own, you should know that you’ll need to remove other parts of the engine as well as special tools to make the repair properly. This is an advanced repair job and requires a great deal of skill. If you’re new to home car repair, you may not want to attempt it yourself. There are many other options, such as hiring a mechanic.
Installation instructions
While there are no universal installation instructions for belt tensioners, the manufacturer of your car may provide detailed instructions. Before attempting to replace your tensioner, read the manufacturer’s recommended procedures carefully. To install a new tensioner properly, unload the old 1 and take a picture or sketch of how the belt should be routed. Once the old tensioner is out, follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications. Make sure to unload and remove the belt from the tensioner, and follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications to install the new one.
If your car comes with a manual belt tensioner, you can follow the instructions. The manual will have a corresponding guide for installation. When installing a belt tensioner, make sure the manual clearly states the static tension for your particular model. Check that it is in line with the engine relief to ensure proper belt tension. You can then use a 6mm allen key to turn the tensioner clockwise and counterclockwise. Once it is in position, release the tensioner to operate. The belt tensioner should now apply the proper tension to your belt.
Before installing a new belt tensioner, make sure you read the manual completely. You should follow these steps carefully to avoid any problems with the tensioner. If the tensioner has failed, you must replace it immediately. A new belt tensioner will help you ensure proper performance of your accessory belt drive system. If you are installing a new multi-ribbed belt, you should replace the tensioner as well. However, it is important to note that replacing the belt tensioner is a complicated process and requires a mechanic to be able to safely remove the belt from the engine.
To install a second stage drive belt, walk the belt onto the input drive and generator. Ensure that the belt is seated properly in the grooves of the pulleys. Next, replace the input drive belt and right and left Drive Disk covers. Test the machine to ensure that it is working properly. If it doesn’t, replace the original drive belt. After installing the new belt, you may want to read the manual again to make sure it is in perfect condition.

